Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions
Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Boiling Point, Vapour Pressure, Freezing Point, Saturated Vapour Pressure, Partial Vapour Pressure, Variation of Vapour Pressure with Temperature and, Standard Boiling Point
Important Questions on Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions
Which of the following plots does not represent the behaviour of an ideal binary liquid solution?
The vapour pressure vs. temperature curve for a solution solvent system is shown below.
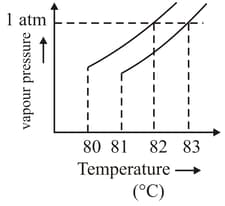
The boiling point of the solvent is _____°C.
Which of the given statements is correct with respect to a liquid?
Two liquids and boil at and respectively. Which of them has a higher vapour pressure at ?
Why boiling point of water is increased on the addition of sodium chloride into it?
Why does vapour pressure of a liquid decrease when a non-volatile solute is added into it?
Why is the vapour pressure of a liquid constant at a constant temperature?
The vapour pressure of ethanol is torr at . if of ethanol is . Calculate the temp. when then vapour pressure is torr.
The vapour pressure of ethanol is at if of ethanol is . Calculate the temperature when the vapour pressure is . [Use relation ]
Define the vapour pressure of a liquid. What happens to the vapour pressure when the dissolved solute is non-volatile.
Describe the relation between vapour pressure and surface area.
Why is the vapour pressure of a solution of glucose in water lower than that of water?
If an aqueous solution of glucose is allowed to freeze, then crystals of which will be seperated out first?
An aqueous solution of methanol in water has vapour pressure
Why boiling of an egg or cooking of rice in an open vessel takes more time at a hill station?
The boiling point of carbon tetrachloride is and its heat of vaporisation is . Calculate the vapour pressure of carbon tetrachloride in atmospheres at .
Why is liquid ammonia bottle first cooled in ice before opening it ?
